Citation:
摘要:
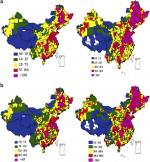
Multi-year inventories of carbonaceous aerosol emissions from biomass open burning at a high spatial resolution of 0.5° × 0.5° have been constructed in China using GIS methodology for the period 1990–2005. Black carbon (BC) emissions have increased by 383.03% at an annual average rate of 25.54% from 14.05 Gg in 1990 to 67.87 Gg in 2005; while organic carbon (OC) emissions have increased by 365.43% from 57.37 Gg in 1990 to 267.00 Gg in 2005. Through the estimation period, OC/BC ratio for biomass burning was averagely 4.09, suggesting that it was not the preferred control source from a climatic perspective. Spatial distribution of BC and OC emissions were similar, mainly concentrated in three northeastern provinces, central provinces of Shandong, Jiangsu, Anhui and Henan, and southern provinces of Guangxi, Guangdong, Hunan and Sichuan basin, covering 24.89% of China’s territory, but were responsible for 63.38% and 67.55% of national BC and OC emissions, respectively.
