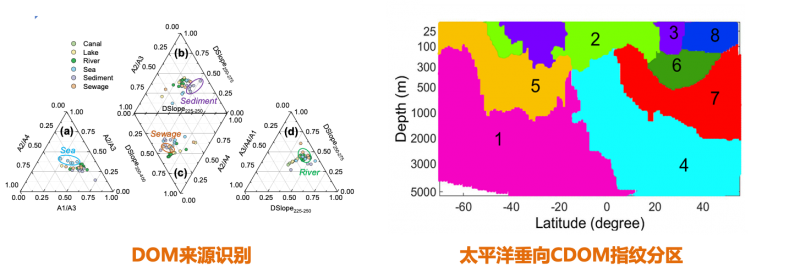
有机质的紫外-可见光谱如同指纹,能反映水文地质、植被、土地利用、人为活动、水体自身营养状况等因素的影响。研制有机质多化学态紫外-可见光谱指纹水质识别技术与装备,揭示水色蕴含的有机质及颗粒物、藻类等信息,应用于河流、海洋中有机质的来源、迁移转化机制、行为效应观测。
代表性论文:
(1) Gu, X. et al., Insights into molecules of natural organic matter binding with a Copper(II) cation: Interpretation based on FT-ICR-MS and differential UV–Vis absorbance spectra. ACS ES&T Water, 3(10): 3315-3322. (2023).
(2) Yan, M. et al., Effects of charging on the chromophores of dissolved organic matter from the Rio Negro basin. Water Res 59, 154-164. (2014).
(3) Mo, S. et al., Unveiling ongoing biogeochemical dynamics of CDOM from surface to deep ocean. (Revising)
