自1852年Bouguer−Lambert−Beer经验定律建立以来一直是光度学的基本原理。针对其不适用于真实环境非均质体系的难题,探索利用量子化学计算、瞬态光学、高分辩质谱、NMR等先进研究方法,从光的量子性识别非均有机质紫外-可见吸收光信号蕴含的总量-组分-活性信息。以真实水环境观测为目标,研制满足实验室科研、在线、遥感观测功能需求的智能感知新方法、新技术及关键仪器装备。
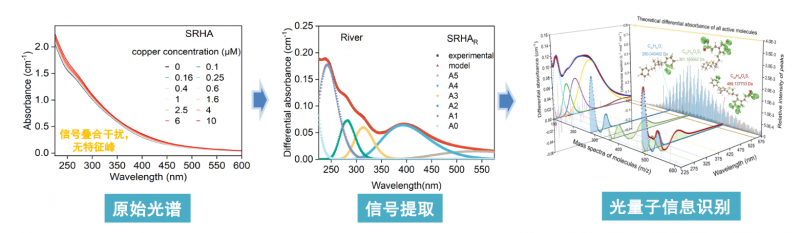
有机质紫外-可见光谱量子信息识别
代表性论文:
(1) Yan, M. et al., Absorptivity inversely proportional to spectral slope in CDOM. Environ Sci Technol, 59(4), 7156-7164 (2025).
(2) Zhang, C. et al., Interpreting pH-dependent differential UV/VIS absorbance spectra to characterize carboxylic and phenolic chromophores in natural organic matter. Water Res 244, 120522 (2023).
(3) Yan, M. et al., Investigating the features in differential absorbance spectra of NOM associated with metal ion binding: A comparison of experimental data and TD-DFT calculations for model compounds. Water Res 124, 496-503 (2017).
