Citation:
摘要:
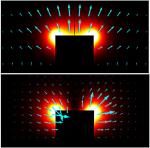
Subwavelength plasmonic waveguides are the most promising candidates for developing planar photonic circuitry platforms. In this study a subwavelength metallic ridge waveguide is numerically and experimentally investigated. Differing from previous plasmonic waveguides, the metallic strip of the subwavelength ridge waveguide is placed on a thick metal film. It is found that the surface-plasmon-polariton (SPP) waveguide modes result from the coupling of the corner modes in the two ridge corners. The bottom metal film has a great influence on the SPP modes, and nearly all the evanescent fields of the SPP modes are tightly confined outside the ridge waveguide. Simulations show that 50% of the total power flow in the SPP mode can be confined outside the ridge waveguide with an area of only about λ 2/20. The propagation length is still about 10 times the plasmon wavelength. Through comparison with a metallic strip placed directly on the dielectric substrate, the proposed ridge waveguide exhibits a much higher sensing performance. This plasmonic ridge waveguide with deep-subwavelength outside-field confinements is of significance in a range of nano-optics applications, especially in nanosensing.
